天堂之门 (Heaven’s Gate)
写在前面
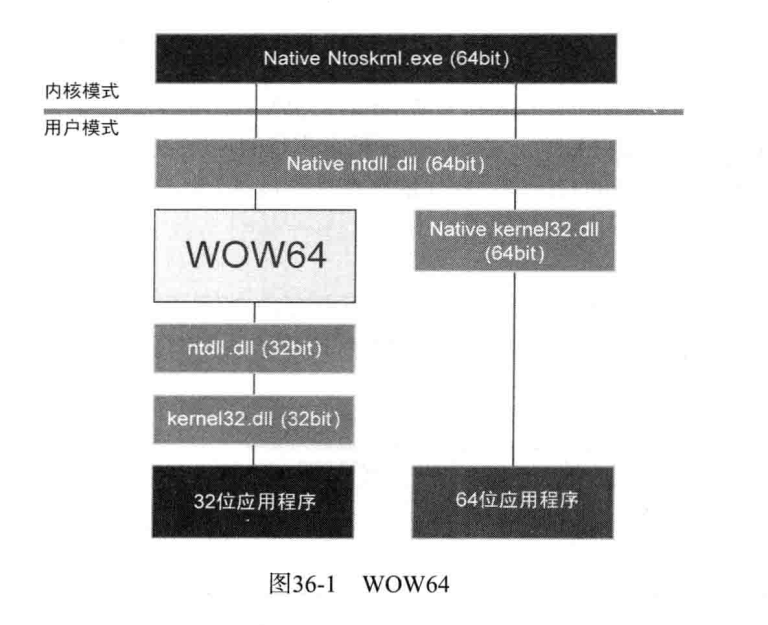
天堂之门技术一种在32位进程运行64位代码的技术,其作用是有一定的反调试能力,但是主要还是在恶意代码执行上面,并却能过一些比较表层的检测,这是一个算比较老的技术了,但是其原理值得我们思考,主要利用的就是64位的windows对32位程序的兼容性,是通过WOW64来将32位进程转化为64位的进程来运行的,我们可以模拟WOW64的工作来达到运行64位汇编代码的能力。下面这张图就是32位和64位程序运行的大致过程,可以看到WOW64就是起到了一个转化器的作用,实际运行还是会放到64位中去运行。
32位切换64位的关键代码
32位->64位
push 0x33
push _next_x64_code ;即将执行64位代码的坐标
retf64位->32位
push 0x23
push _nexr_x86_code
retfq ; q代码qword
ret ; 32位代码原理:
由于64位之后不在需要用段寄存器来寻址,因为一个64位的寄存器已经足够寻到内存空间内所有的地址,所以cs有了一个新的功能用于切换cpu运行汇编的模式,0x33位64位模式,0x23为32模式。
天堂之门的实现步骤
1.实现32位->64位的转换
2.获取PEB地址 FS:[60] (64位之后PEB放在了60的位置,32位则放在了30位置)
3.读取64位ntdll
4.在ntdll获取相关函数( ldrLoad)
5.构造64位的函数调用
6.由ldrLoad获取kernel32
7.获得常用的64位函数的位置
shellcode的制作工具
这里采用python的keystone来将我们写的汇编代码转化为机器码,值得注意的是在换机器吗时要先把汇编中的地址为非硬编码的换成硬编码,比如上面的_next_x64_code这个地址我们把它换成0x12345678 一共4字节,如果是64位的就换成8字节,先随便换一个占上位置,后面再找出这些位置将其替换成正确的位置。
from keystone import *
code = '''
mov esp,ebx
pop ebx
ret
'''
ks = Ks(KS_ARCH_X86 , KS_MODE_32)#只用变后面那一个位置x64 x32
asm,cnt =ks.asm(code)
print(code)
for b in asm:
print('0x' + hex(b)[2:].upper(), end=', ')
代码部分
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
// 拷贝函数 这个函数的目的就是可以在32位的情况下可以使用64位的地址来拷贝
void memcpy64(UINT64 dst, UINT64 src, UINT64 sz)
{
/*retf表示远返回,该指令会从栈顶取出一个返回地址,再取出一个cs段选择子
[bits 32] 这个在代码中是不存在的
push 0x33
push _next_x64_code
retf
0x6A, 0x33, 0x68, 0x78, 0x56, 0x34, 0x12, 0xCB,
[bits 64]表示接下来的汇编要以64位模式编译
push rsi
push rdi
mov rsi,src
mov rdi,dst
mov rcx,sz
rep movsb #rsi->rdi
pop rdi
pop rsi
[bits 64]
push 0x23
push _next_x32_code
retfq q代表qword返回的是64位的地址
[bits 32]
ret 用python把keystone
*/
BYTE code[] = {
0x6A,
0x33, 0x68, 0x78, 0x56, 0x34, 0x12,
0xCB,
0x56, 0x57,
0x48, 0xBE, 0x88, 0x77, 0x66, 0x55, 0x44, 0x33, 0x22, 0x11,
0x48, 0xBF, 0x88, 0x77, 0x66, 0x55, 0x44, 0x33, 0x22, 0x11,
0x48, 0xB9, 0x88, 0x77, 0x66, 0x55, 0x44, 0x33, 0x22, 0x11,
0xF3, 0xA4,
0x5E, 0x5F,
0x6A, 0x23,
0x68, 0x78, 0x56, 0x34, 0x12,
0x48, 0xCB,
0xC3
};
// 申请一个内存空间用来放上面写法shellcode 这里用static是否合理
static UINT32 ptr = NULL;
if (!ptr) {
// 这里的VirtualAlloc与VirtualAllocEx的区别是后一个可以加一个进程句柄,申请指定进程的空间
ptr = (UINT32)VirtualAlloc(NULL, sizeof(code), MEM_COMMIT | MEM_RESERVE, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE);
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(code); i++) {
((PBYTE)ptr)[i] = code[i];
}
}
// 补全shellcode中的参数信息
*(UINT32*)(ptr + 3) = (UINT32)(ptr + 8);
*(UINT64*)(ptr + 12) = (UINT64)src;
*(UINT64*)(ptr + 22) = (UINT64)dst;
*(UINT64*)(ptr + 32) = (UINT64)sz;
*(UINT32*)(ptr + 47) = (UINT32)(ptr + 53);
// 将ptr转化为函数指针,让shellcode跑起来,完成这个函数的功能
((void(*)())ptr)();
}
// 找到PEB 64位中gs:[0x30]指向TEB,gs:[0x60]指向PEB
// 由于不太清楚PEB64在32位程序的大小所以用void*吧
void GetPEB(void *PEB64)
{
/*
mov rax,gs:[0x60]
mov [rsi],rax
*/
BYTE code[] = {
// mov rsi, PEB64 0x12345678
0xBE, 0x78, 0x56, 0x34, 0x12,
0x6A,
0x33, 0x68, 0x78, 0x56, 0x34, 0x12,
0xCB,
0x65, 0x48, 0xA1, 0x60, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0,0x67 ,0x48, 0x89, 0x6,
0x6A, 0x23,
0x68, 0x78, 0x56, 0x34, 0x12,
0x48, 0xCB,
0xC3
};
// 这申请内存的部分可以单独弄函数
static UINT32 ptr = NULL;
if (!ptr) {
// 这里的VirtualAlloc与VirtualAllocEx的区别是后一个可以加一个进程句柄,申请指定进程的空间
ptr = (UINT32)VirtualAlloc(NULL, sizeof(code), MEM_COMMIT | MEM_RESERVE, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE);
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(code); i++) {
((PBYTE)ptr)[i] = code[i];
}
}
*(UINT32*)(ptr + 1) = (UINT32)PEB64;
*(UINT32*)(ptr + 8) = (UINT32)(ptr + 13);
*(UINT32*)(ptr + 31) = (UINT32)(ptr + 37);
((void(*)())ptr)();
}
/*
从PEB+0x18获取Ldr的地址
从Ldr+0x10获取InLoadOrderModuleList地址
遍历InLoadOrderModuleList获取模块基址
通过模块基址获取模块名,并与moduleName比对,比对成功则返回该模块基址
*/
UINT64 GetModuleHandle64(const WCHAR* ModleName)
{
// 这里用UINT64而不是UINT64* ,因为UINT64*在32位的程序中是4字节的,而PEB64的地址是8字节的
UINT64 PEB64 = 0;
GetPEB(&PEB64);
UINT64 Ldr = 0;
memcpy64((UINT64)&Ldr, PEB64 + 0x18, 8);
UINT64 InLoadOrderModuleList = 0;
memcpy64((UINT64)&InLoadOrderModuleList, Ldr+0x10, 8);
// 保存头节点
UINT64 pHead = InLoadOrderModuleList;
UINT64 pNode = 0;
memcpy64((UINT64)&pNode, pHead, 8);
while (pNode != pHead) {
UINT64 pName = 0;
memcpy64((UINT64)&pName, pNode+96, 8);
if(pName){
WCHAR tmp_ModleName[32] = { 0, };
memcpy64((UINT64)tmp_ModleName, pName, 64);
if (!lstrcmpiW(tmp_ModleName, ModleName)) {
UINT64 base = 0;
memcpy64((UINT64)&base, pNode + 48, 8);
return base;
}
}
// 将node中存的地址给node就实现了链表的遍历
memcpy64((UINT64)&pNode, pNode, 8);
}
return 0;
}
// 通过读取hModle的导出表
UINT64 MyGetProcAddress64(UINT64 hModle, const char* func)
{
IMAGE_DOS_HEADER dos;
memcpy64((UINT64)&dos, hModle, sizeof(dos));
IMAGE_NT_HEADERS64 nt;
memcpy64((UINT64)&nt, dos.e_lfanew + hModle, sizeof(nt));
IMAGE_EXPORT_DIRECTORY EAT;
memcpy64((UINT64)&EAT,nt.OptionalHeader.DataDirectory[0].VirtualAddress + hModle, sizeof(EAT));
for (int i = 0; i < EAT.NumberOfNames; i++) {
DWORD pName = 0;
memcpy64((UINT64)&pName, hModle + (EAT.AddressOfNames + i * 4), 4);
char Name[64] = { 0, };
memcpy64((UINT64)Name, (UINT64)(hModle+pName), (UINT64)64);
if (!lstrcmpA(Name, func)) {
// 这里对于导出表的处理还不熟悉 大概需要 由addressofName-索引->addressofNameOrdinals->addressofFunctions
WORD ordinal = 0;
memcpy64((UINT64)&ordinal, hModle + (EAT.AddressOfNameOrdinals + i * 2), 2);
UINT32 funcAddress = 0;
memcpy64((UINT64)&funcAddress, hModle + (EAT.AddressOfFunctions + ordinal * 4), 4);
return hModle + funcAddress;
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
构造一个64位的调用
前四个参数从左往右依次存放到rcx, rdx, r8, r9寄存器中
后面的参数从右往左依次入栈
rsp与最后一个参数之间直接需要保留大小为20字节的空间,被调函数可能会使用
*/
// 这个32位的argc可能是错的
UINT64 X64Call(UINT64 proc, UINT32 argc, ...)
{
BYTE code[] = {
0x53, 0x89, 0xE3, 0x83, 0xE4, 0xF8,
0x6A, 0x33, 0x68, 0x78, 0x56, 0x34, 0x12,
0xCB,
/*
push rsi
push rdi
mov rsi,args
mov rcx,[rsi]
mov rdx,[rsi+8]
mov r8,[rsi+16]
mov r9,[rsi+24]
mov rax,argc
args_start:
cmp rax,4
jle args_end
mov rdi,[(rax-1)*8+rsi]
push rdi
dec rax
jmp args_start
args_enda:
mov rax,proc
sub rsp,32
call rax
mov rdi,&retn
mov [rdi],rax
pop rdi
pop rsi
*/
0x56, 0x57,
0x48, 0xBE, 0x88, 0x77, 0x66, 0x55, 0x44, 0x33, 0x22, 0x11, 0x48, 0x8B, 0xE, 0x48, 0x8B, 0x56, 0x8, 0x4C, 0x8B, 0x46, 0x10, 0x4C, 0x8B, 0x4E, 0x18,
0x48, 0xB8, 0x88, 0x77, 0x66, 0x55, 0x44, 0x33, 0x22, 0x11, 0x48, 0x83, 0xF8, 0x4, 0x7E, 0xB, 0x48, 0x8B, 0x7C, 0xC6, 0xF8, 0x57, 0x48, 0xFF, 0xC8, 0xEB, 0xEF,
0x48, 0xB8, 0x88, 0x77, 0x66, 0x55, 0x44, 0x33, 0x22, 0x11, 0x48, 0x83, 0xEC, 0x20, 0xFF, 0xD0,
0x48, 0xBF, 0x88, 0x77, 0x66, 0x55, 0x44, 0x33, 0x22, 0x11, 0x48, 0x89, 0x7,
0x5F, 0x5E,
/*
push 0x23
push 0x12345678
retfq
mov esp,ebx
pop ebx
ret
*/
0x6A, 0x23,
0x68, 0x78, 0x56, 0x34, 0x12,
0x48,
0xCB,
0x89, 0xDC, 0x5B,
0xC3
};
static UINT32 ptr = NULL;
if (!ptr) {
// 这里的VirtualAlloc与VirtualAllocEx的区别是后一个可以加一个进程句柄,申请指定进程的空间
ptr = (UINT32)VirtualAlloc(NULL, sizeof(code), MEM_COMMIT | MEM_RESERVE, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE);
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(code); i++) {
((PBYTE)ptr)[i] = code[i];
}
}
// 这一步是
UINT64* args = (UINT64*)(&argc+1);
UINT64 ret = 0;
*(UINT32*)(ptr + 9) = (UINT32)(ptr + 14);
*(UINT64*)(ptr + 18) = (UINT64)args;
*(UINT64*)(ptr + 43) = (UINT64)argc;
*(UINT64*)(ptr + 70) = (UINT64)proc;
*(UINT64*)(ptr + 86) = (UINT64)&ret;
*(UINT32*)(ptr + 102) = (UINT32)(ptr + 108);
((void(*)())ptr)();
return ret;
}
// 用于构造一个UTF字符串
char* MakeUTFStr(const char* str) {
UINT32 len = lstrlenA(str);
char* out = (char*)malloc(16 + (len + 1) * 2);
*(UINT16*)(out) = (UINT16)(len * 2); //Length
*(UINT16*)(out + 2) = (UINT16)((len + 1) * 2); //Max Length
UINT16* outstr = (UINT16*)(out + 16);
for (UINT32 i = 0; i <= len; i++) outstr[i] = str[i];
*(UINT64*)(out + 8) = (UINT64)(out + 16);
return out;
}
// 加载kernal32
UINT64 GetModuleLDREntry(const wchar_t* name) {
UINT64 ptr;
GetPEB(&ptr);
memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&ptr), ptr + 24, 8);//PTR -> PPEB_LDR_DATA LoaderData;
UINT64 start = ptr + 16;
memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&ptr), ptr + 16, 8);//PTR -> LIST_ENTRY64 InLoadOrderModuleList.FirstBlink
while (start != ptr) {
UINT64 tmp;
memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&tmp), ptr + 96, 8); //TMP -> UNICODE_STRING Basename -> Buffer
if (tmp) {
wchar_t kek[32];
memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)kek, tmp, 60); //KEK = Basename
if (!lstrcmpiW(name, kek))return ptr;
}
memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&ptr), ptr, 8); //PTR -> Flink
}
return 0;
}
UINT64 GetKernel32() {
static UINT64 kernel32 = 0;
if (kernel32) return kernel32;
UINT64 ntdll = GetModuleHandle64(L"ntdll.dll");
UINT64 LdrLoadDll = MyGetProcAddress64(ntdll, "LdrLoadDll");
char* str = MakeUTFStr("kernel32.dll");
int ret0 = X64Call(LdrLoadDll, 4, (UINT64)0, (UINT64)0, (UINT64)str, (UINT64)(&kernel32));
return kernel32;
}
// 这部分注释掉的是Getkernel32失败,返回值是0的时候,我查阅大佬博客的代码
// 为什么会返回失败呢,由于在32位的情况下,64位的kernel的内存空间会被私有化没办法访问,导致无法获取到地址具体情况我还没分析清楚等知识更加渊博的时候再来考虑。
//UINT64 GetModuleLDREntry(const wchar_t* name) {
// UINT64 ptr;
// GetPEB(&ptr);
// memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&ptr), ptr + 24, 8);//PTR -> PPEB_LDR_DATA LoaderData;
//
// UINT64 start = ptr + 16;
// memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&ptr), ptr + 16, 8);//PTR -> LIST_ENTRY64 InLoadOrderModuleList.FirstBlink
//
// while (start != ptr) {
// UINT64 tmp;
// memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&tmp), ptr + 96, 8); //TMP -> UNICODE_STRING Basename -> Buffer
//
// if (tmp) {
// wchar_t kek[32];
// memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)kek, tmp, 60); //KEK = Basename
//
// if (!lstrcmpiW(name, kek))return ptr;
// }
// memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&ptr), ptr, 8); //PTR -> Flink
// }
// return 0;
//}
//UINT64 GetKernel32() {
// static UINT64 kernel32 = 0;
// if (kernel32)return kernel32;
//
// UINT64 ntdll = GetModuleHandle64(L"ntdll.dll");
// UINT64 LdrLoadDll = MyGetProcAddress64(ntdll, "LdrLoadDll");
//
// char* str = MakeUTFStr("kernel32.dll");
// X64Call(LdrLoadDll, 4, (UINT64)0, (UINT64)0, (UINT64)(unsigned)str, (UINT64)(unsigned)(&kernel32));
//
// if (!kernel32) {
// UINT64 LdrGetKnownDllSectionHandle = MyGetProcAddress64(ntdll, "LdrGetKnownDllSectionHandle");
// UINT64 NtMapViewOfSection = MyGetProcAddress64(ntdll, "NtMapViewOfSection");
// UINT64 NtUnmapViewOfSection = MyGetProcAddress64(ntdll, "NtUnmapViewOfSection");
// UINT64 NtFreeVirtualMemory = MyGetProcAddress64(ntdll, "NtFreeVirtualMemory");
// const WCHAR * dlls[] = { L"kernelbase.dll", L"kernel32.dll", L"user32.dll" };
//
// for (int i = 1; i < 3; i++) {
// UINT64 section = 0;
// UINT64 base = 0;
// UINT64 size = 0;
// X64Call(LdrGetKnownDllSectionHandle, 3, (UINT64)(unsigned)(dlls[i]), (UINT64)0, (UINT64)(unsigned)(§ion));
// X64Call(NtMapViewOfSection, 10, section,
// (UINT64)-1, (UINT64)(unsigned)(&base), (UINT64)0, (UINT64)0, (UINT64)0,
// (UINT64)(unsigned)(&size), (UINT64)2, (UINT64)0, (UINT64)PAGE_READONLY);
//
// IMAGE_DOS_HEADER* dos = (IMAGE_DOS_HEADER*)base;
// IMAGE_NT_HEADERS64* nt = (IMAGE_NT_HEADERS64*)(base + dos->e_lfanew);
// UINT64 imagebase = nt->OptionalHeader.ImageBase;
//
// UINT64 zero = 0;
// X64Call(NtFreeVirtualMemory, 4, (UINT64)-1, (UINT64)(unsigned)(&imagebase), (UINT64)(unsigned)(&zero), (UINT64)MEM_RELEASE);
// X64Call(NtUnmapViewOfSection, 2, (UINT64)-1, (UINT64)(unsigned)(&base));
// }
//
// X64Call(LdrLoadDll, 4, (UINT64)0, (UINT64)0, str, (UINT64)(unsigned)(&kernel32));
//
// for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
// UINT64 base = GetModuleHandle64(dlls[i]);
// IMAGE_DOS_HEADER* dos = (IMAGE_DOS_HEADER*)base;
// IMAGE_NT_HEADERS64* nt = (IMAGE_NT_HEADERS64*)(base + dos->e_lfanew);
//
// UINT64 r = X64Call(base + nt->OptionalHeader.AddressOfEntryPoint, 3, base, (UINT64)DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH, (UINT64)0);
//
// UINT64 ldr = GetModuleLDREntry(dlls[i]);
//
// UINT64 flags;
// memcpy64((UINT64)(unsigned)(&flags), ldr + 104, 8);
// flags |= 0x000080000; //LDRP_PROCESS_ATTACH_CALLED
// flags |= 0x000004000; //LDRP_ENTRY_PROCESSED
// memcpy64(ldr + 104, (UINT64)(unsigned)(&flags), 8);
//
// WORD loadcount = -1;
// memcpy64(ldr + 112, (UINT64)(unsigned)(&loadcount), 2);
// }
// }
// return kernel32;
//}
// 利用前面的函数
UINT64 GetProcAddress64(UINT64 hModule, const char* func)
{
static UINT64 ke32GetProcAddress = 0;
if (!ke32GetProcAddress) {
ke32GetProcAddress = MyGetProcAddress64(GetModuleHandle64(L"kernel32"), "GetProcAddress");
}
return X64Call(ke32GetProcAddress, 2, hModule, (UINT64)func);
}
UINT64 LoadLibrary64(const char* name)
{
static UINT64 LoadLibraryA = 0;
if (!LoadLibraryA) LoadLibraryA = GetProcAddress64(GetKernel32(), "LoadLibraryA");
return X64Call(LoadLibraryA, 1, (UINT64)name);
}
void Test() {
UINT64 kernel32 = GetKernel32();
UINT64 user32 = LoadLibrary64("user32.dll");
UINT64 MessageBox64 = GetProcAddress64(user32, "MessageBoxA");
X64Call(MessageBox64, 4, (UINT64)NULL, (UINT64)"Wowowowowow", (UINT64)"Wowowowowow", (UINT64)NULL);
}
int main() {
Test();
}小结
天堂之门对于刚学习完PEB结构的我来说还是比较有挑战性的,写完这些代码对于PEB,底层的程序执行逻辑认识以及shellcode的编写能力有很大的提升,固然还有一些疑问还未解决,比如对kernel32的加载认识还是比较的模糊,我想这将会是我继续学习下去的动力。