ollvm总结
ollvm介绍
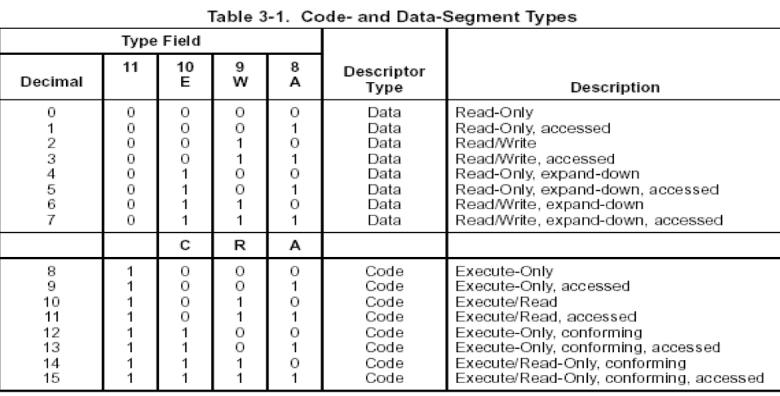
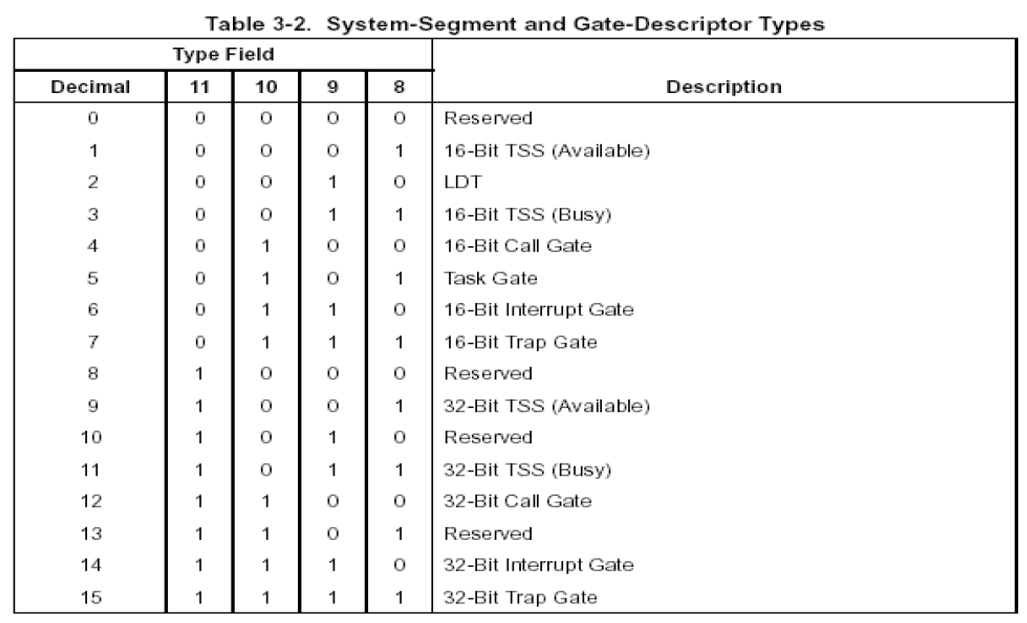
OLLVM中有三种保护方案:BCF(Bogus Control Flow,中文名虚假控制流)、FLA(Control Flow Flattening,中文名控制流平坦化)、SUB(Instructions Substitution,中文名指令替换)
这些保护方案就是字面意思,下面给出他们的加了保护之后ida显示的代码块的截图就可以大概了解了
未混淆版:
FLA版:
BCF版:
SUB版:
全开:
ollvm环境搭建
ollvm其中最影响分析的当属控制流平坦化fla了,在解开fla之前得先了解一下,这个程序是如何编译出来的。我这里就用的下面的链接里的方法编译出能可以ollvm的clang编译器
https://www.jianshu.com/p/9136f7257e46
这里我用跟链接里相同的环境,只是在
修改代码时,得把char换成uint8_t。
编译完成后就可以看到在bin目录下看到clang的可执行文件
这时就有一个问题了,为什么这里编译后的clang能进行ollvm处理代码?
这里简单说一下clang+llvm的编译器组合,注意这里说的llvm与ollvm不一样,一个现代编译器的结构如下:

之所以能产生上面图中的代码是因为在代码优化部分进行了处理,当编译器前端分析完写好的代码就会产生叫LLVM IR(Intermediate Representation)的中间代码,产生的中间代码会在代码优化部分进行优化。
具体是怎么优化的呢?
LLVM Pass是代码优化过程中的一个重要部分,LLVM pass就是代码优化中的一个个模块,在代码优化的过程中,就像流水线一样呈线性排列的对生成的中间语言LLVM IR进行优化,第一个pass处理完就会交给下一个pass,直到完成代码的优化。
详细的过程可以看下面这个哥的文章
https://kiprey.github.io/2020/06/LLVM-IR-pass/#简介
clang相关命令
基本命令
代码→LLVM IR
clang -S -emit-llvm hello.cpp -o hello.ll
clang -c -emit-llvm hello.cpp -o hello.bc这两种后缀的都是IR中间原因其中.ll文件是可以阅读的文本而.bc文件则是二进制的机器码,它们作用都一样,都是用来进行优化的中间代码,只是存在状态不同。
LLVM IR→(优化后)LLVM IR
opt -load LLVMObfuscator.so -S hello.ll -o hello_opt.ll-load加载指定的Pass集合
-S输出LLVM IR而不是LLVM字节码
LLVM IR→可执行文件
clang hello_opt.ll -o helloollvm混淆指令
查看所有pass集合,值得注意的是用load产生加载的集合与这里直接显示的集合不同的是,这里显示的显示的集合可以不用load参数就可以调用
opt - load - help;clang的-mllvm的参数意思是在代码进行优化的时候要执行的命令参数,也就是要执行的opt的命令
虚假控制流(Bogus Control Flow)
- mllvm -bcf : 激活虚假控制流
- mllvm -bcf_loop=3 : 混淆次数,这里一个函数会被混淆3次,默认为 1
- mllvm -bcf_prob=40 : 每个基本块被混淆的概率,这里每个基本块被混淆的概率为40%,默认为 30 %
clang -mllvm -bcf -mllvm -bcf_loop=3 -mllvm -bcf_prob=40 hello.cpp -o hello_bcf控制流平坦化(Control Flow Flattening)
- mllvm -fla : 激活控制流平坦化
- mllvm -split : 激活基本块分割
- mllvm -split_num=3 : 指定基本块分割的数目
clang -mllvm -fla -mllvm -split -mllvm -split_num=3 hello.cpp -o hello_fla指令替换(Instruction Substitution)
- mllvm -sub : 激活指令替代
- mllvm -sub_loop=3 : 混淆次数,这里一个函数会被混淆3次,默认为 1次
clang -mllvm -sub -mllvm -sub_loop=3 hello.cpp -o hello_sub去混淆
angr版
脚本来源https://github.com/cq674350529/deflat
进行了一点修改,修复了一些bug吧,因为每个混淆后的无用的代码块不能确定大小,所以每次运行的时候要进行一定的调整。
当能成功找到所有后继块之后脚本就算成功运行了,注意下面的代码并不能直接执行,这里贴在这里是为了便于观看,核心逻辑都在下面的代码里。
脚本的运行原理:
- 首先确定代码的开始和结束位置,然后交给angr分析出
CFG图,cfg图是一种数据结构,类似于ida的代码块那样的,只不过是他的抽象形式。然后遍历整个有向图,找到入度为0的地方即为入口块,出度为0的地方即为retn块。 - 然后就是找到主分发块,有时主分发块就是入口块的一部分,而原程序是通过入度数量大于1来判定主分发块的,最终就导致了主分发就是入口块,这就是原来脚本不能跑起来的根本原因了。
解决办法是什么呢?通过patch一个jmp跳转指令来人为的构造一个块,把这个分发块构造出来。
为什么通jmp指令就能人为的构造一个块呢?是因为angr分析出来的CFG有向图是以jmp指令来分割的,也就是是如果有一个jmp指令,那么angr就会把它分析成一个块。这样就能成功识别出来了。
- 通过主分发块找他的前支就只有入口块,和预处理块。然后再通过预处理块去找到所有有用块,但是这里找到的有用块里面的不是所有都是有用的,有很多长得很相似的块都是可以直接nop的,所以要找出来,在那个脚本里是直接进行进行大小判断的小于一定的大小就会直接nop,但是在不同的程序里,这个大小是变化的,所以这就是另一个有bug的地方。
找到所有有用块之后,就相当于把所有块进行了分类,分为可以nop掉的块,入口块,主分发块,预处理块和有有用块
然后就开始对每个有用块进行模拟执行,找到每个有用块之间的关系,就完成了整个代码的还原了
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
sys.path.append("..")
import argparse
import angr
import pyvex
import claripy
import struct
from collections import defaultdict
import am_graph
from util import *
import logging
logging.getLogger('angr.state_plugins.symbolic_memory').setLevel(logging.ERROR)
# logging.getLogger('angr.sim_manager').setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
def get_relevant_nop_nodes(supergraph, pre_dispatcher_node, prologue_node, retn_node):
# relevant_nodes = list(supergraph.predecessors(pre_dispatcher_node))
relevant_nodes = []
nop_nodes = []
for node in supergraph.nodes():
if supergraph.has_edge(node, pre_dispatcher_node) and node.size > 16 and node.addr != prologue_node.addr:
# XXX: use node.size is faster than to create a block
relevant_nodes.append(node)
continue
if node.addr in (prologue_node.addr, retn_node.addr, pre_dispatcher_node.addr):
continue
nop_nodes.append(node)
return relevant_nodes, nop_nodes
def symbolic_execution(project, relevant_block_addrs, start_addr, hook_addrs=None, modify_value=None, inspect=False,
hook_size=None, pre_dispatcher_node=None):
def retn_procedure(state):
ip = state.solver.eval(state.regs.ip)
project.unhook(ip)
return
def statement_inspect(state):
expressions = list(
state.scratch.irsb.statements[state.inspect.statement].expressions)
if len(expressions) != 0 and isinstance(expressions[0], pyvex.expr.ITE):
state.scratch.temps[expressions[0].cond.tmp] = modify_value
state.inspect._breakpoints['statement'] = []
if hook_addrs is not None:
for hook_addr in hook_addrs:
skip_length = hook_size[hook_addr]
project.hook(hook_addr, retn_procedure, length=skip_length)
state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=start_addr, remove_options={
angr.sim_options.LAZY_SOLVES})
if inspect:
state.inspect.b(
'statement', when=angr.state_plugins.inspect.BP_BEFORE, action=statement_inspect)
sm = project.factory.simulation_manager(state)
sm.step()
# 设置要执行的圈数
flag = 0
while len(sm.active) > 0:
for active_state in sm.active:
if active_state.addr in relevant_block_addrs:
return active_state.addr
# 避免死循环
if active_state.addr == pre_dispatcher_node.addr:
flag = flag + 1
if flag == 2:
return None
sm.step()
return None
def main():
DEBUG = True
end = 0
start = 0
if DEBUG:
filename = "./rushB"
start = 0x4005A0
end = 0x400A71
else:
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="deflat control flow script")
parser.add_argument("-f", "--file", help="binary to analyze")
parser.add_argument(
"--addr", help="address of target function in hex format")
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.file is None or args.addr is None:
parser.print_help()
sys.exit(0)
filename = args.file
start = int(args.addr, 16)
project = angr.Project(filename, load_options={'auto_load_libs': False})
# do normalize to avoid overlapping blocks, disable force_complete_scan to avoid possible "wrong" blocks
# cfg = project.analyses.CFGFast(normalize=True, force_complete_scan=False)
cfg = project.analyses.CFGFast(
start=start >> 12 << 12,
end=end,
force_complete_scan=False,
normalize=True,
)
target_function = cfg.functions.get(start)
# A super transition graph is a graph that looks like IDA Pro's CFG
supergraph = am_graph.to_supergraph(target_function.transition_graph)
base_addr = project.loader.main_object.mapped_base >> 12 << 12
# get prologue_node and retn_node
prologue_node = None
retn_node = None
for node in supergraph.nodes():
if supergraph.in_degree(node) == 0:
prologue_node = node
if supergraph.out_degree(node) == 0:
retn_node = node
# tset retn_node
# block = project.factory.block(retn_node.addr, size=retn_node.size)
# for ins in block.capstone.insns:
# print(ins.insn.mnemonic)
if prologue_node is None or prologue_node.addr != start:
print("Something must be wrong...")
sys.exit(-1)
# #######################################
# 对main_dispatcher_node和pre_dispatcher_node的处理需要注意,这两正确基本可以跑出相关块,必要的时候这两个块可以相等
# #######################################
main_dispatcher_node = list(supergraph.successors(prologue_node))[0]
# main_dispatcher_node = prologue_node
# pre_dispatcher_node = main_dispatcher_node
for node in supergraph.predecessors(main_dispatcher_node):
if node.addr != prologue_node.addr:
pre_dispatcher_node = node
break
relevant_nodes, nop_nodes = get_relevant_nop_nodes(
supergraph, pre_dispatcher_node, prologue_node, retn_node)
print('*******************relevant blocks************************')
print('prologue: %#x' % start)
print('main_dispatcher: %#x' % main_dispatcher_node.addr)
print('pre_dispatcher: %#x' % pre_dispatcher_node.addr)
print('retn: %#x' % retn_node.addr)
relevant_block_addrs = [node.addr for node in relevant_nodes]
print('relevant_blocks:', [hex(addr) for addr in relevant_block_addrs])
print('*******************symbolic execution*********************')
relevants = relevant_nodes
relevants.append(prologue_node)
relevants_without_retn = list(relevants)
relevants.append(retn_node)
relevant_block_addrs.extend([prologue_node.addr, retn_node.addr])
flow = defaultdict(list)
patch_instrs = {}
# 注意符号执行找相关块的时候是把体类所有的函数调用都给hook了的,所以当调用的函数会修改符号执行的流程的时候这时的脚本是跑不了的,得把文件本身修了
for relevant in relevants_without_retn:
print('-------------------dse %#x---------------------' % relevant.addr)
block = project.factory.block(relevant.addr, size=relevant.size)
has_branches = False
hook_addrs = []
hook_size = {}
for ins in block.capstone.insns:
if project.arch.name in ARCH_X86:
if ins.insn.mnemonic.startswith('cmov'):
# only record the first one
if relevant not in patch_instrs:
patch_instrs[relevant] = ins
has_branches = True
elif ins.insn.mnemonic.startswith('call'):
hook_addrs.append(ins.insn.address)
hook_size[ins.insn.address] = len(ins.insn.bytes)
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM:
if ins.insn.mnemonic != 'mov' and ins.insn.mnemonic.startswith('mov'):
if relevant not in patch_instrs:
patch_instrs[relevant] = ins
has_branches = True
elif ins.insn.mnemonic in {'bl', 'blx'}:
hook_addrs.append(ins.insn.address)
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM64:
if ins.insn.mnemonic.startswith('cset'):
if relevant not in patch_instrs:
patch_instrs[relevant] = ins
has_branches = True
elif ins.insn.mnemonic in {'bl', 'blr'}:
hook_addrs.append(ins.insn.address)
if has_branches:
tmp_addr = symbolic_execution(project, relevant_block_addrs,
relevant.addr, hook_addrs, claripy.BVV(1, 1), True, hook_size=hook_size, pre_dispatcher_node=pre_dispatcher_node)
if tmp_addr is not None:
flow[relevant].append(tmp_addr)
tmp_addr = symbolic_execution(project, relevant_block_addrs,
relevant.addr, hook_addrs, claripy.BVV(0, 1), True, hook_size=hook_size, pre_dispatcher_node=pre_dispatcher_node)
if tmp_addr is not None:
flow[relevant].append(tmp_addr)
else:
tmp_addr = symbolic_execution(project, relevant_block_addrs,
relevant.addr, hook_addrs, hook_size=hook_size, pre_dispatcher_node=pre_dispatcher_node)
if tmp_addr is not None:
flow[relevant].append(tmp_addr)
# tmp_addr = symbolic_execution(project, relevant_block_addrs,
# relevant.addr, hook_addrs, claripy.BVV(1, 1), True, hook_size=hook_size, pre_dispatcher_node=pre_dispatcher_node)
# if tmp_addr is not None:
# flow[relevant].append(tmp_addr)
# tmp_addr = symbolic_execution(project, relevant_block_addrs,
# relevant.addr, hook_addrs, claripy.BVV(0, 1), True, hook_size=hook_size, pre_dispatcher_node=pre_dispatcher_node)
# if tmp_addr is not None:
# flow[relevant].append(tmp_addr)
print('************************flow******************************')
for k, v in flow.items():
print('%#x: ' % k.addr, [hex(child) for child in v])
print('%#x: ' % retn_node.addr, [])
print('************************patch*****************************')
with open(filename, 'rb') as origin:
# Attention: can't transform to str by calling decode() directly. so use bytearray instead.
origin_data = bytearray(origin.read())
origin_data_len = len(origin_data)
recovery_file = filename + '_recovered'
recovery = open(recovery_file, 'wb')
# patch irrelevant blocks
for nop_node in nop_nodes:
fill_nop(origin_data, nop_node.addr - base_addr,
nop_node.size, project.arch)
fill_nop(origin_data, main_dispatcher_node.addr - base_addr, main_dispatcher_node.size, project.arch)
# remove unnecessary control flows
for parent, childs in flow.items():
if len(childs) == 1:
parent_block = project.factory.block(parent.addr, size=parent.size)
last_instr = parent_block.capstone.insns[-1]
size_last = len(last_instr.insn.bytes)
# add
last_two_instr = parent_block.capstone.insns[-2]
size_last_two = len(last_two_instr.insn.bytes)
# nop_instructions = last_two_instr.address
nop_size = size_last + size_last_two
file_offset = last_two_instr.address - base_addr
# patch the last instruction to jmp
if project.arch.name in ARCH_X86:
# fill_nop(origin_data, file_offset,
# last_instr.size, project.arch)
fill_nop(origin_data, file_offset, nop_size, project.arch)
patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(last_two_instr.address, childs[0], 'jmp')
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM:
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm(last_instr.address, childs[0], 'b')
if project.arch.memory_endness == "Iend_BE":
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM64:
# FIXME: For aarch64/arm64, the last instruction of prologue seems useful in some cases, so patch the next instruction instead.
if parent.addr == start:
file_offset += 4
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm64(last_instr.address + 4, childs[0], 'b')
else:
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm64(last_instr.address, childs[0], 'b')
if project.arch.memory_endness == "Iend_BE":
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value)
else:
instr = patch_instrs[parent]
file_offset = instr.address - base_addr
# patch instructions starting from `cmovx` to the end of block
size = 0
fill_nop(origin_data, file_offset, parent.addr +
parent.size - base_addr - file_offset, project.arch)
if project.arch.name in ARCH_X86:
# patch the cmovx instruction to jx instruction
patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(instr.address, childs[0], instr.mnemonic[len('cmov'):])
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value, size)
file_offset += 6
# patch the next instruction to jmp instrcution
patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(instr.address + 6, childs[1], 'jmp')
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value, size)
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM:
# patch the movx instruction to bx instruction
bx_cond = 'b' + instr.mnemonic[len('mov'):]
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm(instr.address, childs[0], bx_cond)
if project.arch.memory_endness == 'Iend_BE':
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value, size)
file_offset += 4
# patch the next instruction to b instrcution
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm(instr.address + 4, childs[1], 'b')
if project.arch.memory_endness == 'Iend_BE':
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value, size)
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM64:
# patch the cset.xx instruction to bx instruction
bx_cond = instr.op_str.split(',')[-1].strip()
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm64(instr.address, childs[0], bx_cond)
if project.arch.memory_endness == 'Iend_BE':
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value, size)
file_offset += 4
# patch the next instruction to b instruction
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm64(instr.address + 4, childs[1], 'b')
if project.arch.memory_endness == 'Iend_BE':
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value, size)
assert len(origin_data) == origin_data_len, "Error: size of data changed!!!"
recovery.write(origin_data)
recovery.close()
print('Successful! The recovered file: %s' % recovery_file)
for nop_node in nop_nodes:
fill_nop(origin_data, nop_node.addr - base_addr,
nop_node.size, project.arch)
# remove unnecessary control flows
for parent, childs in flow.items():
if len(childs) == 1:
parent_block = project.factory.block(parent.addr, size=parent.size)
last_instr = parent_block.capstone.insns[-1]
file_offset = last_instr.address - base_addr
# patch the last instruction to jmp
if project.arch.name in ARCH_X86:
fill_nop(origin_data, file_offset,
last_instr.size, project.arch)
patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(last_instr.address, childs[0], 'jmp')
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM:
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm(last_instr.address, childs[0], 'b')
if project.arch.memory_endness == "Iend_BE":
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM64:
# FIXME: For aarch64/arm64, the last instruction of prologue seems useful in some cases, so patch the next instruction instead.
if parent.addr == start:
file_offset += 4
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm64(last_instr.address + 4, childs[0], 'b')
else:
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm64(last_instr.address, childs[0], 'b')
if project.arch.memory_endness == "Iend_BE":
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value)
else:
instr = patch_instrs[parent]
file_offset = instr.address - base_addr
# patch instructions starting from `cmovx` to the end of block
fill_nop(origin_data, file_offset, parent.addr +
parent.size - base_addr - file_offset, project.arch)
if project.arch.name in ARCH_X86:
# patch the cmovx instruction to jx instruction
patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(instr.address, childs[0], instr.mnemonic[len('cmov'):])
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value)
file_offset += 6
# patch the next instruction to jmp instrcution
patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(instr.address + 6, childs[1], 'jmp')
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value)
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM:
# patch the movx instruction to bx instruction
bx_cond = 'b' + instr.mnemonic[len('mov'):]
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm(instr.address, childs[0], bx_cond)
if project.arch.memory_endness == 'Iend_BE':
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value)
file_offset += 4
# patch the next instruction to b instrcution
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm(instr.address + 4, childs[1], 'b')
if project.arch.memory_endness == 'Iend_BE':
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value)
elif project.arch.name in ARCH_ARM64:
# patch the cset.xx instruction to bx instruction
bx_cond = instr.op_str.split(',')[-1].strip()
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm64(instr.address, childs[0], bx_cond)
if project.arch.memory_endness == 'Iend_BE':
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value)
file_offset += 4
# patch the next instruction to b instruction
patch_value = ins_b_jmp_hex_arm64(instr.address + 4, childs[1], 'b')
if project.arch.memory_endness == 'Iend_BE':
patch_value = patch_value[::-1]
patch_instruction(origin_data, file_offset, patch_value)
assert len(origin_data) == origin_data_len, "Error: size of data changed!!!"
recovery.write(origin_data)
recovery.close()
print('Successful! The recovered file: %s' % recovery_file)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()采用angr的缺点
由于angr脚本里是直接以块为起点,模拟执行来找到下一个块的,如果在这个块之前还产生了对这个块的执行流程产生了影响的事件,那么本次模拟处理的结果就是不准确的。
unicorn版
为什么要用unicorn呢?
因为unicorn就相当于一个虚拟cpu,所以处理的细微程度远远高于angr的代码块级,修复出来的代码精度更高。如果能用unicorn从入口块开始完整模拟执行到retn块结束,就能相对完整的还原整个代码。
由于unicorn的模拟代码还没写完,这里就暂时不贴出来了(等我写完,就补上
import re
import idaapi
import idautils
NOP_Code = 0xD503201F
# 添加一个黑名单块 去掉那些不用修复的块 需要手动添加
black_list = [0x105077A2C,]
def print_blocks_info(blocks):
for block in blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
# 从基本块中查找指定位置的块
def find_block(blocks, ea):
for block in blocks:
if block.start_ea <= ea and block.end_ea > ea:
return block
return None
def get_function_blocks(func_ea):
func = idaapi.get_func(func_ea)
if not func:
return None
# 存放所有的代码块
blocks = []
flowchart = idaapi.FlowChart(func)
for block in flowchart:
# 过滤调黑名单块
if block.start_ea not in black_list:
blocks.append(block)
else:
print("black_list block: 0x%08x" % block.start_ea)
return blocks
def get_instructions_in_block(block):
instructions = []
for head in idautils.Heads(block.start_ea, block.end_ea):
instructions.append((head, idc.GetDisasm(head)))
return instructions
# 读取一个代码块的数据
def read_data(start, end):
start_address = start
size = end - start
data = ida_bytes.get_bytes(start_address, size)
return data
# 写入读取的数据
def write_data(start, data):
start_address = start
size = len(data)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(start_address, data)
return
# 用unicorn先装载整个函数的代码,然后分别模拟执行每个真实块
from unicorn import *
from unicorn.arm64_const import *
from capstone import *
def emulate_code(jmping_blocks, dispatch_blocks):
jmping_table = {}
# 回调函数,当执行每一条指令时被调用
def hook_code(uc, address, size, user_data):
# print(">>> Tracing instruction at 0x%x, instruction size = 0x%x" %(address, size))
# 获取当前指令的字节码
instruction = uc.mem_read(address, size)
for i in md.disasm(instruction, address):
# 检查是否是 bl 指令
# print("0x%x:\t%s\t%s" %(i.address, i.mnemonic, i.op_str))
if i.mnemonic == 'bl':
uc.reg_write(UC_ARM64_REG_PC, address + size)
# 如果到达分发块的位置,就停止模拟执行
if address >= dispatch_blocks[0].start_ea + 0x8 and address <= dispatch_blocks[0].end_ea:
uc.emu_stop()
return
# 对之后的代码进行模拟执行 如果发生异常就跳过指令
return
uc = Uc(UC_ARCH_ARM64, UC_MODE_LITTLE_ENDIAN)
md = Cs(CS_ARCH_ARM64, CS_MODE_ARM)
# 分配一块内存
address = idaapi.get_imagebase()
uc.mem_map(address, 1024 * 1024 * 1024)
# 写入数据
code_start = ida_funcs.get_func(entry_blocks[0].start_ea).start_ea
code_end = ida_funcs.get_func(entry_blocks[0].end_ea).end_ea
code = read_data(code_start, code_end)
print("code_start: 0x%08x" % (address+code_start))
print("address: 0x%08x" % address)
uc.mem_write(code_start, code)
# 初始化栈空间
stack_start = 0x80000000
stack_size = 0x10000 * 8
stack_sp = 0x80000000 + 0x10000 * 6
uc.mem_map(stack_start,stack_size)
uc.reg_write(UC_ARM64_REG_SP,stack_sp)
# 设置hook
uc.hook_add(UC_HOOK_CODE, hook_code)
# 注意这里隐含提前执行了入口块来初始化环境 开始模拟执行每个的真实块
index = 0
while True:
block = jmping_blocks[index]
start_address = jmping_blocks[index].start_ea
# print("start_address: 0x%08x" % start_address)
while True:
error = None
try:
uc.emu_start(start_address, -1)
except UcError as e:
error = e
# print("Error:触发异常但是继续执行 %s" % e)
# 修改PC寄存器, 跳过当前执行报错的汇编代码
start_address = uc.reg_read(UC_ARM64_REG_PC) + 4
continue
finally:
if error == UC_ERR_OK or error == None:
break
# 读取返回值
W8 = uc.reg_read(UC_ARM64_REG_W8)
jmping_table[hex(block.start_ea)] = [hex(W8)]
# print("0x%08x: 0x%08x" % (block.start_ea, W8))
# 修改迭代变量
index += 1
if index >= len(jmping_blocks):
break
print(jmping_table)
return jmping_table
# 遍历代码块 找到入度为0的代码块
def find_entry_blocks(blocks):
entry_blocks = []
for block in blocks:
if list(block.preds()) == []:
entry_blocks.append(block)
return entry_blocks
# 遍历代码块 找到出度为0的代码块
def find_exit_blocks(blocks):
# ios 退出块跟其他程序有点不同,需要进行修改
_objc_autoreleaseReturnValue_addr = idc.get_name_ea_simple("_objc_autoreleaseReturnValue")
exit_blocks = []
for block in blocks:
if list(block.succs()) == []:
# 如果结果是ios的退出块,需要把前面的一个块作为退出块
if block.start_ea == _objc_autoreleaseReturnValue_addr:
pre_blocks = list(block.preds())
if(len(pre_blocks) != 1):
# list后出现的块还有这个返回块本身
print("Error: ios exit block num is not 1")
print_blocks_info(pre_blocks)
exit(1)
else:
exit_blocks.append(pre_blocks[0])
else:
exit_blocks.append(block)
return exit_blocks
# 遍历代码 匹配入度为1 出度为2的代码块
def find_if_blocks(blocks):
if_blocks = []
for block in blocks:
if len(list(block.preds())) == 1 and len(list(block.succs())) == 2:
if_blocks.append(block)
return if_blocks
# 遍历代码 匹配入度为2 出度为2的代码块
def find_dispatch_blocks(blocks):
dispatch_blocks = []
for block in blocks:
if len(list(block.preds())) == 2 and len(list(block.succs())) == 2:
dispatch_blocks.append(block)
return dispatch_blocks
# 遍历代码 匹配入度为n 出度为1的代码块
def find_predispatch_blocks(blocks):
predispatch_blocks = []
for block in blocks:
if len(list(block.preds())) >= 3 and len(list(block.succs())) == 1:
predispatch_blocks.append(block)
return predispatch_blocks
# 遍历代码块 找到入度为1 出度为1的代码块 去除返回分发块的代码块
def find_real_blocks(blocks, exit_blocks):
real_blocks = []
small_blocks = []
exit_block_start = exit_blocks[0].start_ea
for block in blocks:
block_start = block.start_ea
# 代码块的大小 去除返回分发块的代码块 去除返回块
block_size = block.end_ea - block.start_ea
if block_size <= 4:
small_blocks.append(block)
if len(list(block.preds())) == 1 and len(list(block.succs())) == 1 and block_size > 4 and block_start != exit_block_start:
real_blocks.append(block)
return real_blocks, small_blocks
# 查找剩下的代码块
def find_remaining_blocks(blocks, entry_blocks, exit_blocks, dispatch_blocks, predispatch_blocks, if_blocks):
left_blocks = []
for block in blocks:
if block not in entry_blocks and block not in exit_blocks and block not in dispatch_blocks and block not in predispatch_blocks and block not in if_blocks:
left_blocks.append(block)
return left_blocks
# 读取 if_blocks和dispatch_blocks 中的代码块 获取代码块中的指令 并进行正则匹配取出于条件跳转相关的值:
def match_if_blocks(if_blocks, dispatch_blocks):
all_blocks = if_blocks + dispatch_blocks
jump_table = {}
jmp_index = 0
jump_addr = 0
for block in all_blocks:
instructions = get_instructions_in_block(block)
for (ea, disasm) in instructions:
# 匹配 MOV 指令 这个寄存器和下面的跳转指令在每个不同的ollvm中可能有变化
if "MOV W9" in disasm:
re_tmp = re.search(r'#(0x[A-Fa-f0-9]+)', disasm)
if re_tmp:
jmp_index = int(re_tmp.group(1),16)
if "B.EQ" in disasm:
match_addr = re.search(r'loc_([A-Fa-f0-9]+)', disasm)
if match_addr:
jump_addr = int(match_addr.group(1),16)
if jmp_index and jump_addr:
jump_table[hex(jmp_index)] = hex(jump_addr)
else:
print("Error: jmp_index or jump_addr is None")
return jump_table
# 会产生条件跳转的代码块 branch_blocks
# C9 95 83 52 MOV W9, #0x6EBB1CAE
# 69 D7 AD 72
# 08 C2 90 52 MOV W8, #0x80978610
# E8 12 B0 72
# 4A 01 00 71 SUBS W10, W10, #0
# 08 01 89 1A CSEL W8, W8, W9, EQ
# E8 17 00 B9 STR W8, [SP,#0x60+var_4C]
# A9 BB 91 52 MOV W9, #0x7D008DDD
# 09 A0 AF 72
# 48 B2 91 52 MOV W8, #0x99268D92
# C8 24 B3 72
# 4A 01 00 72 ANDS W10, W10, #1
# 08 11 89 1A CSEL W8, W8, W9, NE
# 68 56 00 B9 STR W8, [X19,#0x54]
def find_branch_blocks(blocks):
match_instructions = [
"MOV",
"MOV",
"*",
"CSEL",
"ST"
]
branch_blocks = []
branch_block_adds = []
for block in blocks:
instructions = get_instructions_in_block(block)
for index in range(len(instructions)):
branch_block_flag = True
branch_block_add = 0
# 先判断一下剩下的代码是否足够一次匹配
if len(match_instructions) >= len(instructions[index:]):
break
# 匹配指令
for ii in range(len(match_instructions)):
# 记录ii == 0的位置信息
if ii == 2:
branch_block_add = instructions[index+ii][0]
if match_instructions[ii] == "*":
continue
if match_instructions[ii] not in instructions[index+ii][1]:
branch_block_flag = False
break
if branch_block_flag:
branch_block_adds.append(hex(branch_block_add))
branch_blocks.append(block)
break
return branch_blocks, branch_block_adds
# 匹配 jmp_status 和代码块之间的关系
def match_jmp_status(jmping_blocks, dispatch_blocks, branch_blocks, branch_adds):
# jmping_branch_table = {}
jmping_table = {}
# 先处理全部块,给每个块赋值一个初始映射
jmping_table = emulate_code(jmping_blocks, dispatch_blocks)
# 再修改会出现分支的块
for branch_add in branch_adds:
branch_add = int(branch_add,16)
branch_block = find_block(branch_blocks, branch_add)
mov0_add = branch_add -16
mov1_add = branch_add -8
cmp_add = branch_add
mov_add = branch_add + 4
store_add = branch_add + 8
# 获取条件判断处的汇编指令
ins = idc.GetDisasm(mov_add)
# 切割字符串获取操作符 和操作数
ins = ins.split("; ")[0]
operator = ins.split(" ")[0]
operand = ins.split(" ")[1].split(", ")
# 根据CSEL指令来确定使用的寄存器
reg0 = operand[-3]
reg1 = operand[-2]
mov0_ins = idc.GetDisasm(mov0_add)
mov1_ins = idc.GetDisasm(mov1_add)
mov_value0 = int(re.search(r'#(0x[A-Fa-f0-9]+)', mov0_ins).group(1),16)
mov_value1 = int(re.search(r'#(0x[A-Fa-f0-9]+)', mov1_ins).group(1),16)
if reg0 in mov0_ins:
jmping_table[hex(branch_block.start_ea)] = [hex(mov_value0)]
jmping_table[hex(branch_block.start_ea)].append(hex(mov_value1))
elif reg0 in mov1_ins:
jmping_table[hex(branch_block.start_ea)] = [hex(mov_value1)]
jmping_table[hex(branch_block.start_ea)].append(hex(mov_value0))
else:
print("Error: reg0 not in mov0_ins or mov1_ins")
exit(1)
return jmping_table
# 生成调用关系
def generate_call_relationship(jmping_table, jmp_table):
call_relationship = {}
for key,jmping_single_array in jmping_table.items():
# print(key,jmping_single_array)
call_relationship[key] = []
for const_about_addr in jmping_single_array:
call_relationship[key].append(jmp_table[const_about_addr])
return call_relationship
# 用于生成B跳转指令的机器码
def generate_b_instruction_machine_code(jmp_addr, current_addr):
differentialOffset = (jmp_addr - current_addr)//4
patch_code = 0
if differentialOffset < 0:
patch_code = (differentialOffset&0xffffff)+ 0x17000000
else:
patch_code = (differentialOffset&0xffffff)+ 0x14000000
return patch_code
# 利用keystone来生成汇编指令的机器码
from keystone import *
def generate_machine_code(asm_ins,addr=0):
ks = Ks(arch=KS_ARCH_ARM64, mode=KS_MODE_LITTLE_ENDIAN)
encoding, count = ks.asm(asm_ins,addr=addr)
encoding_dword = int.from_bytes(encoding, 'little')
return encoding_dword
# patch 代码块 首先去掉结尾的跳转指令 然后切割代码块
def patch_blocks(jmping_blocks, call_relationship, branch_adds):
for block in jmping_blocks:
block_start = block.start_ea
block_end = block.end_ea - 4
jmp_adds = call_relationship[hex(block_start)]
# 判断是否为纯跳转
if len(jmp_adds) == 1:
# patch 跳转指令
jmp_add = int(jmp_adds[0],16)
patch_code = generate_b_instruction_machine_code(jmp_add, block_end)
print("patch code:0x%08x :0x%08x" % (block_end,patch_code))
idaapi.set_cmt(block_end, ("0x%08x" % patch_code), 0)
ida_bytes.patch_dword(block_end, patch_code)
# 判断跳转指令之前的两个代码是否可以nop
ins00 = idc.GetDisasm(block_end - 12)
ins01 = idc.GetDisasm(block_end - 4)
if "MOV W8, " in ins00 and "ST" in ins01:
idaapi.set_cmt(block_end - 12, ("0x%08x" % NOP_Code), 0)
idaapi.set_cmt(block_end - 8, ("0x%08x" % NOP_Code), 0)
idaapi.set_cmt(block_end - 4, ("0x%08x" % NOP_Code), 0)
ida_bytes.patch_dword(block_end - 12, NOP_Code)
ida_bytes.patch_dword(block_end - 8, NOP_Code)
ida_bytes.patch_dword(block_end - 4, NOP_Code)
for branch_add in branch_adds:
branch_add = int(branch_add,16)
branch_block = find_block(jmping_blocks, branch_add)
branch_block_start = branch_block.start_ea
branch_block_end = branch_block.end_ea - 4
jmp_adds = call_relationship[hex(branch_block_start)]
# 判断是否为条件跳转
if len(jmp_adds) == 2:
cmp_add = branch_add
mov_add = branch_add + 4
store_add = branch_add + 8
# 获取条件判断处的汇编指令
ins = idc.GetDisasm(mov_add)
# 切割字符串获取操作符 和操作数
ins = ins.split("; ")[0]
operator = ins.split(" ")[0]
operand = ins.split(" ")[1].split(", ")
# 拼接跳转指令
jmp_if_ins = "B"+operand[-1] + " " + jmp_adds[0]
jmp_else_ins = "B"+" "+jmp_adds[1]
# 要进行patch的地址
branch00_add = 0
branch01_add = 0
# 如果不是末尾调用 需要单独切割代码块 剩下部分的代码整体上移
if branch_block_end - cmp_add != 0xc:
print("Error: branch_block_end - branch_add != 0xc")
print_blocks_info([branch_block])
idaapi.set_cmt(mov_add, jmp_adds[0], 0)
idaapi.set_cmt(store_add, jmp_adds[1], 0)
# 将从代码块的末尾到条件判断处的代码整体上移
move_start = branch_add + 12
move_end = branch_block_end
code = read_data(move_start, move_end)
write_data(mov_add, code)
# 修改要进行patch的地址
branch00_add = branch_block_end - 0x8
branch01_add = branch_block_end - 0x4
else:
branch00_add = mov_add
branch01_add = store_add
# 生成跳转指令的机器码
print("jmp_if_ins: "+jmp_if_ins)
print("jmp_else_ins: "+jmp_else_ins)
jmp_if_ins_machine_code = generate_machine_code(jmp_if_ins,branch00_add)
jmp_else_ins_machine_code = generate_machine_code(jmp_else_ins,branch01_add)
# 进行patch
print("patch code:0x%08x :0x%08x" % (branch00_add,jmp_if_ins_machine_code))
print("patch code:0x%08x :0x%08x" % (branch01_add,jmp_else_ins_machine_code))
idaapi.set_cmt(mov_add, ("0x%08x" % jmp_if_ins_machine_code), 0)
idaapi.set_cmt(store_add, ("0x%08x" % jmp_else_ins_machine_code), 0)
idaapi.set_cmt(branch_block_end, ("0x%08x" % NOP_Code), 0)
ida_bytes.patch_dword(branch00_add, jmp_if_ins_machine_code)
ida_bytes.patch_dword(branch01_add, jmp_else_ins_machine_code)
ida_bytes.patch_dword(branch_block_end, NOP_Code)
else:
print("Error: branch_adds is not 2")
exit(1)
# 将无用的块nop掉
def nop_blocks(blocks):
for block in blocks:
block_start = block.start_ea
block_end = block.end_ea
for add in range(block_start,block_end,4):
idaapi.set_cmt(add, ("0x%08x" % NOP_Code), 0)
ida_bytes.patch_dword(add, NOP_Code)
# func_ea = idc.get_name_ea_simple('_encryptionDeviceId') # 用你的函数名替换 'function_name'
# 获取当前窗口中光标所在位置的地址
current_address = idc.get_screen_ea()
func_ea = idc.get_func_attr(current_address, idc.FUNCATTR_START)
blocks = get_function_blocks(func_ea)
# 查找代码入口和出口
entry_blocks = find_entry_blocks(blocks)
exit_blocks = find_exit_blocks(blocks)
if len(entry_blocks) == 1:
print('Entry blocks:')
for block in entry_blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
else:
print('Entry blocks num error: %d' % len(entry_blocks))
for block in entry_blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
exit(1)
if len(exit_blocks) == 1:
print('Exit blocks:')
for block in exit_blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
else:
# 如果多个退出块的入度为同一个块 则重新设置退出块为他们的父块
parent_block = list(exit_blocks[0].preds())[0]
for block in exit_blocks:
if list(block.preds())[0].start_ea != parent_block.start_ea:
# 如果不是同一个块就退出
print('Exit blocks num error: %d' % len(exit_blocks))
for tmp in exit_blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(tmp.start_ea), hex(tmp.end_ea)))
exit(1)
exit_blocks = [parent_block]
# 查找分发块和预分发块
dispatch_blocks = find_dispatch_blocks(blocks)
predispatch_blocks = find_predispatch_blocks(blocks)
if len(dispatch_blocks) == 1:
print('Dispatch blocks:')
for block in dispatch_blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
else:
print('Dispatch blocks num error: %d' % len(dispatch_blocks))
for block in dispatch_blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
if len(predispatch_blocks) == 1:
print('Predispatch blocks:')
for block in predispatch_blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
else:
print('Predispatch blocks num error: %d' % len(predispatch_blocks))
for block in predispatch_blocks:
print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
# 查找if块
if_blocks = find_if_blocks(blocks)
print('If blocks num: %d' % len(if_blocks))
# 查找入度为1 出度为1的代码块 去除返回分发块的代码块 过滤函数太小的分支
real_blocks, small_blocks = find_real_blocks(blocks, exit_blocks)
print('real blocks num: %d' % len(real_blocks))
# 会被跳转的块
jmped_blocks = exit_blocks + real_blocks
# 会产生跳转的块 把entry_blocks放在前面,便于后面模拟
jmping_blocks = entry_blocks + real_blocks
print('jmped_blocks num: %d' % len(jmped_blocks))
# 从if_block中匹配 jmp_table 找出一个对应关系
jmp_table = match_if_blocks(if_blocks,dispatch_blocks)
print("jmp_table: %d" % len(jmp_table))
# 检查 jmp_table 的数量是否与 jmped_blocks 的数量相等
# if len(jmp_table) != len(jmped_blocks):
# print('Error: jmp_table 不等于 jmped_blocks')
# exit(1)
# real_blocks 中的条件分支块查找 branch_blocks
branch_blocks, branch_adds = find_branch_blocks(real_blocks)
print('branch blocks num: %d' % len(branch_blocks))
# print(branch_adds)
# for block in branch_blocks:
# print('Start: %s, End: %s' % (hex(block.start_ea), hex(block.end_ea)))
# 匹配 jmp_status 和代码块之间的关系 找出调用关系
jmping_table = match_jmp_status(jmping_blocks, dispatch_blocks, branch_blocks, branch_adds)
print(jmping_table)
# 生成调用关系
call_relationship = generate_call_relationship(jmping_table, jmp_table)
print(call_relationship)
# patch 代码块
patch_blocks(jmping_blocks, call_relationship, branch_adds)
# nop掉无用的块
nop_blocks(if_blocks+dispatch_blocks+predispatch_blocks+small_blocks)
小结
总体而言,ollvm现在已经不算一个很难的问题了,除非ollvm里面有异常处理。但是这种问题实战遇到的情况不多,打ctf遇到的要多一些。